Projects
Lighting Up the Subsurface for Tomorrow’s City: Initiating a Penn State Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) Array for Monitoring Geo/Environmental Hazards
Awarded: 2019 | Project Type: IEE Seed Grant
The Penn State DAS array (PSDASA), a subarray of the FORESEE project, is to revolutionize seismic monitoring of the urban area through a novel use of fiber optic cables to improve hazard assessment and increase early warning capability. We propose to develop a 4 km long DAS array leveraging the existing telecommunication fiber-optic cables (unused, so-called dark fiber) underneath the Penn State campus in State College, PA.
Modeling the Risk of West Nile Virus to Ruffed Grouse Populations in Pennsylvania
Awarded: 2019 | Project Type: IEE Seed Grant
West Nile virus (WNV), a virus transmitted by mosquitoes, causes high mortality in many native birds. As WNV spread through Pennsylvania in 2000-2002, populations of ruffed grouse (Bonasa umbellus) - the Pennsylvania State bird- suffered significant declines. Statewide grouse populations remain at record lows. WNV has been well-studied in human-dominated environments, but epidemiology in woodland systems is little-understood despite population-level declines in vulnerable species.
Practical Photovoltaic Daylighting
Awarded: 2019 | Project Type: IEE Seed Grant
Windows and skylights that generate solar electricity, or that adjust their opacity to control room lighting and solar heat gain, feature prominently in most visions of future energy-efficient building technology. Transparent photovoltaics (PV) and electro/thermochromic glass are currently being pursued to achieve these respective goals, but neither works well at present and both hinge on the development of new materials that are unproven in the building industry.
Quantifying Enhanced Performance of Passive House (PH) over Conventional Buildings
Awarded: 2019 | Project Type: IEE Seed Grant
The Passive House (PH) standard relies on enhancing building envelope performance to minimize thermal and moisture loads of a building. PH can leverage collaborative efforts by different project stakeholders to create an energy-efficient approach in different climates. Although the use of PH concepts may increase initial building construction costs this investment is thought to be returned over time.
Rare Earth Element Enrichment from Mining Wastewater Streams
Awarded: 2019 | Project Type: IEE Seed Grant
Water scarcity and pollution is of global concern. Industrial and mining operations are among largest users of water and one of the largest polluters. Wastewater produced by the mineral and coal industry is an environmental concern due to its total suspended and dissolved solids. So far, this wastewater has been treated as waste. However, such wastewater, on the other hand, contains critical elements such as rare earth elements. Rare earth elements (REE) are vital to the U.S.
Resilient and Energy Efficient Envelopes for Passive House Standard Buildings
Awarded: 2019 | Project Type: IEE Seed Grant
One-third of the energy used to heat a typical house is lost by air leaking through the walls or roof. Consequently, new houses built to standards that require minimal energy to provide thermal comfort rely on airtight building envelopes. While the efficacy of the air barrier in these houses is tested during construction and initial occupancy, there has been no research conducted into the resiliency of these air barriers to minor or major displacements caused by earthquakes, wind or other forces.
Searchable Performance Database for Design of Ultra-High-Performance Envelope (UPHE) Buildings in Varied Climatic Conditions
Awarded: 2019 | Project Type: IEE Seed Grant
The project aims to establish the data fields and data format structure of a database of energy utilization and indoor environment performance metrics of buildings having documented ultrahigh performance building envelope (UHPE) designs and associated heating, ventilation and cooling (HVAC) technologies. With the assistance of personnel from the Passive House Institute (Germany) and North American Passive House Network (NAPHN), the project also seeks to establish an initial data population within the structured database.
The Impact of Ecosystem Change and Resilience on Crop Quality and Farmer Livelihoods – Cloves (Syzygium aromaticum) As a Model
Awarded: 2019 | Project Type: IEE Seed Grant
Specialty crops including fruits, nuts, medicinal plants, and spices represent an important part of the world agricultural economy. Their value is driven not only by availability but also perceived quality as judged by wholesalers, processors, and end-users. In the case of spices and related essential oils, quality is driven by the composition of volatile and non-volatile phytochemicals.
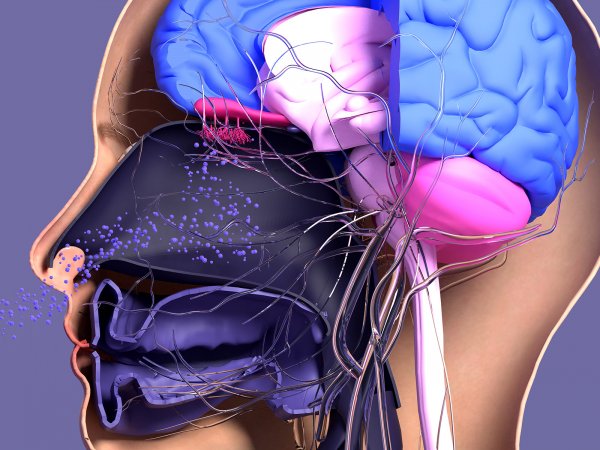
The Role of Olfactory Neuron Death in Particulate Matter-Induced Neurodegeneration
Awarded: 2019 | Project Type: IEE Seed Grant
Air pollution, specifically particulate matter in the 2.5 micron (PM2.5) range, is a ubiquitous health hazard in the developed and developing world. Recently, it has been found that air pollution is not only damaging to lungs, but it is implicated in the development of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) and other neurodegenerative diseases. However, there is no known biological mechanism for air pollution’s effects, and it has been hard to study the mechanistic basis of the damaging effects of particulate matter in the lab.
Uncertainty-Aware Transactive Building Controls
Awarded: 2019 | Project Type: IEE Seed Grant
This project will prototype a building energy control system that enables operations to be optimally coordinated in consideration of uncertainty. Novel algorithmic advancements are proposed to improve the efficiency and scalability of stochastic optimization methods when applied to problems in the high-performance building and electric grid domains. The performance of the uncertainty-aware controller will be evaluated through co-simulation by coupling the controller with detailed, physics-based building energy simulation models.
Visualizing and Experiencing Changes to the Critical Zone
Awarded: 2019 | Project Type: IEE Seed Grant
The purpose of our collaboration is to develop an interdisciplinary program of research aimed at using and understanding how immersive virtual experiences and simulations (IVE&S) can educate the public about the Critical Zone (CZ) and, more specifically, the Food-Energy-Water (FEW) Nexus. We propose that immersive virtual experiences in the CZ (which have never been created) can enhance systems thinking, connections to nature, and emotional states that will facilitate awareness of the FEW Nexus and support for efforts to address related security issues.
Assessing Wetland Characteristics of 0-Order Contributing Areas above Montane Headwater Wetland-Stream Complexes in the Appalachian Mountains – A Pennsylvania Assessment
Awarded: 2018 | Project Type: IEE Seed Grant
Wetland-like features in “0-order” positions above first-order streams are small and often undetected by traditional wetland mapping. As such, these types of wetland features hidden under the canopy have been called ‘cryptic wetlands’. In high-relief landscapes such as the Appalachian Mountains, cryptic wetlands may be associated with seeps, topographic benches or depressions (e.g., the ‘saddle’ between two peaks), or drip lines of overhanging cliffs, and are typically much smaller than 0.5 ha.