LaJeunesse and colleagues receive 2017 Tyge Christiansen Prize
| psu.edu
Three Penn Staters, including Associate Professor of Biology Todd LaJeunesse, his former graduate student Drew Wham, and Director of the Microscopy Facility Gang Ning, have been awarded the 2017 Tyge Christiansen Prize by the International Phycological Society, an organization dedicated to the study of algae.
Fracking wastewater accumulation found in freshwater mussels' shells
| psu.edu
Elevated concentrations of strontium, an element associated with oil and gas wastewaters, have accumulated in the shells of freshwater mussels downstream from fracking wastewater disposal sites, according to researchers from Penn State and Union College.
Energizing the food-energy-water nexus: the fortuitous tale of duckweed
| psu.edu
Rachel Brennan knows how precious of a commodity water is. During her time as the director of Penn State's Eco-Machine, her work has involved a helpful little plant that is impacting the food-energy-water nexus.
Larger cities have smaller water footprint than less populated counterparts
| psu.edu
Global sustainability is important now more than ever due to increasing urban populations and the resulting stress it can have on natural resources. But increased populations in cities may lead to greater efficiency, as a team of Penn State researchers discovered when they analyzed the water footprint of 65 mid- to large-sized U.S. cities.
NSF funds $3 million graduate training program focused on Food-Energy-Water
| psu.edu
The National Science Foundation has awarded a $3 million grant to an interdisciplinary team of Penn State researchers to create a new graduate program that will train students to find solutions to real-world problems facing Food-Energy-Water (FEW) systems.
Diverse symbionts of reef corals have endured since 'age of dinosaurs'
| psu.edu
Coral-algal partnerships have endured numerous climate change events in their long history, and at least some are likely to survive modern-day global warming as well, suggests an international team of scientists.
Penn State hydrologist Elizabeth Boyer honored by American Geophysical Union
| psu.edu
Elizabeth W. Boyer, associate professor of water resources in Penn State's College of Agricultural Sciences, has been honored with the 2018 Witherspoon Lecture Award by the American Geophysical Union.
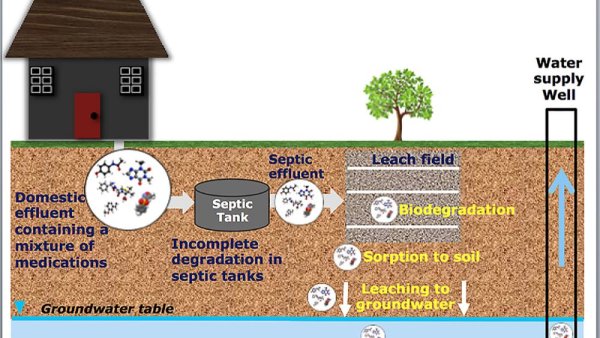
Small amounts of pharmaceuticals found in north central Pa. rural well water
| psu.edu
Drinking water from wells in rural north central Pennsylvania had low levels of pharmaceuticals, according to a study led by Penn State researchers.
Buried Treasure
| psu.edu
Penn State coral reef biologists Mónica Medina and Roberto Iglesias Prieto are studying Varadero reef, off the coast of Colombia, to learn why it is thriving under unusual conditions. With reefs around the world dying off in response to rising ocean temperatures, resilience has become a key concept. What gives some coral species the strength to adapt and bounce back while others perish?
Three new co-funds join Institutes of Energy and the Environment
| psu.edu
Three faculty members recently joined the Institutes of Energy and the Environment (IEE) in three different areas of expertise. Two are in the Donald P. Bellisario College of Communications, and the other is in the College of Earth and Mineral Sciences. This is the first time that IEE has had co-funded faculty in the Bellisario College.
Detective Work: An interdisciplinary dive into the history of American art
| psu.edu
Maggie Davis doesn’t look like a detective. She doesn’t wear a trenchcoat, a fedora or carry a magnifying glass. But the art history major at Penn State is solving a mystery that dates back to the early years of the United States and the birth of the American artistic tradition.
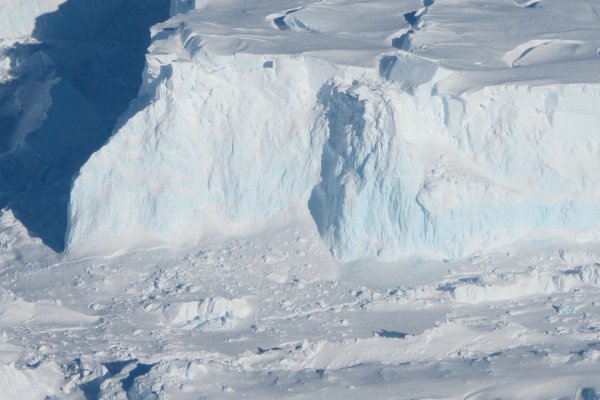
Penn State researchers join international effort to study Antarctic ‘doomsday’ glacier
| alleghenyfront.org
The Thwaites Glacier on the West Antarctic Ice Sheet is about the size of Pennsylvania. Reasonable modeling suggests it could lead to three feet of global sea level rise in the next century so its threatening nickname may not be far off.